Going outside on a sunny day feels wonderful, but the bright light, glare, and UV rays can be tough on your eyes. That’s where a good pair of sunglasses becomes an important tool for protecting your vision and staying comfortable.
When you start looking for new sunglasses, you’ll quickly notice there are so many choices. Besides picking a favorite frame, the real differences often come down to the lenses themselves. You’ll see terms like polarized, mirrored, and photochromic – but what do they mean, and which lens is the best match for your lifestyle?

The type of lens you choose can make a big difference in how well you see, how comfortable you feel, and how well you perform in outdoor activities. Blocking sunlight isn’t the only job lenses do – they each use different technology to deal with specific problems like glare, changing brightness, and contrast.
Knowing what sets each lens apart will help you pick the right pair for your needs, whether you love fishing, drive long distances, mountain bike, or just enjoy a warm, clear day.
This guide explains sunglasses lenses in simple terms, so you can easily decide what’s best for you.
What Types of Sunglasses Lenses Are There?
Start looking at sunglasses, and you’ll realize there’s a lot more to lenses than just colored glass or plastic. The technology inside those curved pieces has gotten very advanced. Traditional dark lenses simply lower brightness, but others are made to handle specific problems like glare, shifting levels of sunlight, or making colors and details easier to see.
You’ll see plenty of extra features (like coatings for less scratching or reflections, special materials for strength, and so on), but there are three main lens types you’ll hear about the most: polarized, mirrored, and photochromic. Each one has its own strengths and is better for certain situations.
Understanding the basics of these three types is a great start to picking sunglasses that really work for you.
Polarized Lenses
Polarized lenses are well-known for cutting down on glare from flat surfaces. They use a special filter that lets most light through but stops blinding glare, especially from water, snow, or roads. Here’s how it works: When sunlight hits something flat, it often bounces off in a straight line – this is the glare that makes things hard to see. The filter inside polarized lenses is lined up a certain way, so it only lets useful light through and blocks the glare. This means you’ll see much more clearly and with less eye strain, especially where there’s a lot of reflected sunlight.
Mirrored Lenses
Mirrored lenses have a shiny surface that reflects much of the light away before it ever reaches your eyes. While they’re very noticeable and stylish, this coating isn’t just for looks – it really helps keep your eyes comfortable in very bright places. The mirror finish makes the lenses darker and blocks more light than regular tinted lenses, which is great for long days spent in the sun. Sometimes, the mirror effect is stronger in some parts of the lens than others, giving you different levels of darkness depending on where you look through the lens.

Photochromic Lenses
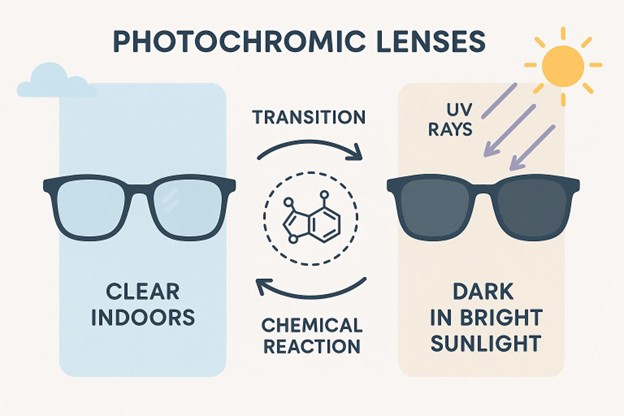
Photochromic lenses, sometimes called transition lenses, change automatically based on how much sunlight they’re exposed to. Indoors or in shade, they’re clear or almost clear. Step out into the sun, and they darken by themselves.
The change happens because of chemicals in the lens that react to UV light. When you step back inside or the sun goes down, the lenses get lighter again. Photochromic lenses are handy for anyone who’s always moving between inside and outside but doesn’t want to keep swapping glasses.
How Do Polarized Lenses Work?
Polarized lenses are made specifically to deal with glare. While regular dark lenses make things look dimmer, polarized lenses use a filter, placed in the lens, that blocks certain light waves. Sunlight reflecting off water, pavement, or snow moves in straight, horizontal lines, mixing to form glare.
The vertical filter in polarized lenses stops this light, cutting glare and letting through the useful light that helps you see clearly. This simple but clever filtering makes a big difference for comfort and safety, especially when you’re outside a lot.
Main Benefits of Polarized Lenses
The biggest plus of polarized lenses is how well they get rid of glare, which is important for both comfort and seeing clearly. By blocking harsh reflected light from water, snow, or roads, these lenses make it easier to see details and spot things that would be hidden by brightness.
This improved comfort means you can spend more time in the sun without your eyes getting tired. Some brands say their polarized lenses block almost all reflected light and also help colors and contrast stand out more, making what you see look sharper and more colorful.
Things to Watch Out for with Polarized Lenses
Polarized lenses are great at cutting glare, but they do have some downsides. They can sometimes make it hard to see screens on devices like your phone, GPS, or car dashboard, because many of these also use polarized light.
When this happens, the screen might look dim or have strange colors. If you need to check digital screens often, this is something to think about.
Also, polarized lenses don’t block more daylight than regular tinted lenses – they’re just better at managing glare. For some activities, if you actually need to see shiny surfaces (like patches of ice while skiing), a non-polarized lens could be more useful. And always check if your lenses offer full UV protection, since polarization and UV filtering are not the same thing.
Best Times to Use Polarized Lenses
Polarized lenses are best anywhere you face a lot of glare. They’re perfect for water sports – like fishing or boating – because they help you see beneath the surface. They’re also very good for skiing, snowboarding, and any activity on snow, since the glare can be strong and blinding.
Drivers can benefit too, especially in bright weather or on wet roads, because these lenses cut down the dangerous reflections that can block your view.
They’re also helpful for outdoor running, cycling, and playing sports on the beach, because they let you see clearly and avoid eye fatigue.

What Do Mirrored Lenses Do?
Mirrored lenses are easy to spot because of their shiny, reflective surface. This shiny finish works by bouncing a lot of light away from the lens, helping keep as much brightness as possible out of your eyes.
The thickness and type of mirror coating decide how much light is reflected, with heavier coatings blocking even more. Mirrored lenses are usually built on top of a tinted base, and both the mirror and the tint help control how much light comes through and what colors you see.
Benefits of Mirrored Lenses
Mirrored lenses are great for lowering the amount of sunlight that gets to your eyes, which helps in very bright and sunny places. They’re often used on snow or water, where the conditions are tough and you need to keep glare and brightness down as much as possible.
The reflective layer may also keep your lenses from scratching easily, depending on the quality. Besides their practical use, mirrored lenses come in many colors and give a bold, stylish look to your sunglasses. They also give you more privacy, since your eyes are harder to see.
Limitations of Mirrored Lenses
While mirrored lenses help with overall brightness, their coating can scratch easily, and any marks can be pretty obvious. Unlike polarized lenses, mirrored lenses don’t single out and block glare from flat surfaces – they only make things generally darker.
The overall performance of mirrored lenses depends a lot on the underlying lens quality and tint. While they cut a lot of light, mirrored lenses don’t adjust automatically to brightness or filter specific glares like polarized or photochromic lenses do.
Best Uses for Mirrored Lenses
Mirrored lenses are perfect for the brightest outdoor situations – on snow, in the mountains, or on open water. They’re also a good pick for cycling or running in the midday sun, as well as driving or motorcycling in strong sunlight. Anytime you expect intense sun and want less light reaching your eyes, mirrored lenses are a smart choice.
How Do Photochromic Lenses Work?
Photochromic lenses offer a special solution for people who move between different light conditions often. These lenses use chemicals that respond to UV rays from the sun.
When you go outside, the chemical reaction makes the lenses darken, taking in more light and protecting your eyes. When you go back inside or UV levels drop, the lenses return to being nearly clear again.
The speed and darkness of this change depend on the weather, temperature, and the type of lens or coating.
Main Benefits of Photochromic Lenses
The best feature of photochromic lenses is their ability to adjust from clear to dark and back again. This means you don’t need different pairs of glasses for different conditions – the lenses do the work for you. They reduce eye strain, since your eyes don’t have to adjust suddenly when going from indoors to outdoors or vice versa.
Photochromic lenses protect from UV rays and are useful for lots of activities involving changing light, like cycling through sun and shadow or skiing down different slopes.
Limitations of Photochromic Lenses
Photochromic lenses sometimes have a delay in adjusting, especially if it’s hot outside. They may not get as dark as sunglass lenses, mainly inside vehicles, since most windshields filter out the UV rays that trigger the darkening.
Photochromic lenses don’t block glare as well as polarized lenses, so for very reflective situations, you might need something stronger. They also might not darken much on bright, cloudy days without a lot of UV rays.
Who Should Use Photochromic Lenses?
If you find yourself moving between indoors and outdoors a lot, photochromic lenses can save you time and trouble. They’re handy for everyday wear, sports with changing light (like trail running or cycling), and activities throughout the day as conditions shift.
If you drive often, however, keep in mind these lenses may not darken much inside your car. Color options can range from gray to brown and sometimes green, so you can pick a look you like.
How Do These Lens Types Compare?
Each lens type has its own role. Polarized lenses are strongest at getting rid of glare. Mirrored lenses are best for making things much darker in bright sun. Photochromic lenses are flexible and adapt to different lighting but are not as useful against strong glare.
When deciding, think about how each lens type changes light, how they deal with glare, and how tough they are. Cost is also different for each, depending on the technology used.
Clarity and Glare Control
If glare is your main issue, polarized lenses are best. They help you see more clearly by blocking the kind of light that makes glare on water or pavement. Mirrored lenses help with brightness and make things look darker, but they don’t specifically stop glare. Photochromic lenses mostly handle changes in light but don’t reduce glare much.
Light Changes and UV Protection
Photochromic lenses excel at adjusting to light, switching from light to dark as needed. Polarized and mirrored lenses stay the same tint all the time; you have to switch them manually if you want different looks. No matter what lens you choose, make sure they offer full UV protection for your eye health. This is not always included, so check the product label.
Durability and Care
Lens toughness depends on the base material and the type of coating. Polycarbonate lenses won’t break easily; glass resists scratches better but is heavier. Mirrored coatings can scratch, and scratches show up quickly.
Polarized film is inside the lens, so the lens itself is strong, but the outside can still scratch. Photochromic coatings can sometimes be more delicate, especially if they are surface treatments. In all cases, lens coatings like anti-reflective and anti-scratch can help. Use a proper cleaning cloth and avoid rough materials to help lenses last longer.
How Prices Compare
Special lenses cost more. Polarized lenses tend to be pricier than just tinted ones. Mirrored coatings add to the price, and photochromic lenses are usually most expensive because of their changing feature. The final price depends on the material, coatings, and brand quality. Cheaper options are available, but you’ll usually get better results with higher-end products.
Which Lens Is Best for You?
- Lots of glare (water, snow, roads): Polarized lenses are the best choice.
- Very strong sunshine: Go for mirrored lenses.
- Changing light (moving from indoors to outdoors): Photochromic lenses offer the most convenience.
- While driving: Polarized lenses help best with road glare, though photochromic is good if you need to switch light levels frequently. Mirrored also helps with bright days.
- Sports with varying light: Photochromic lenses are great for activities like running or cycling in mixed conditions.
- Sports with a lot of glare (fishing, skiing): Polarized is almost always best.
- Personal style: If you like bold colors and shiny looks, mirrored lenses stand out the most.

In the end, which lens type is right for you depends on what you need most and what you find most comfortable.
So, Which Lens Is Right for You?
Now that you know what each lens does, how do you pick the right one? It depends on your routine, the environment where you’ll use them, and what your eyes need.
Choosing the right sunglasses is about finding the balance between comfort, performance, and eye health.
Remember, your main goal is not just to block sunlight – it’s also to see clearly and safely, protect your eyes, and keep them from getting tired. By looking at what’s most important in your daily life, you’ll be able to make the right choice.
Helpful Questions for Picking Lenses
- What will I usually be doing when I wear the sunglasses?
- What kind of light will I face most often? (Bright sun, changing conditions, glare?)
- Is glare a big problem for me?
- Do I want one pair that does everything, or do I need top performance for a specific activity?
- How much do I want to spend?
- Will I need to look at digital screens? (Polarized lenses might not work well with some screens.)
- What look or style do I prefer?
Tips Based on Common Lifestyles
- Love fishing or water sports? Go with polarized lenses to see better through the glare.
- Ski or snowboard often? Polarized or mirrored lenses will keep your vision clear and protect against reflection.
- Drive a lot? Polarized lenses are best for cutting out road glare.
- Cycling or running outdoors in mixed light? Photochromic lenses quickly adjust as you move through sun and shadow.
- For everyday life or frequent indoor/outdoor switching: Photochromic lenses make things simple.
- Always in super-bright places? Mirrored lenses help the most.
- General outdoor use on sunny days: Both polarized and mirrored lenses can help keep your eyes comfortable.

